Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is the #1 cause of vision loss over the age of 50 and impacts the lives of 1 in 8 over the age of 80.
Macular degeneration (AMD) is an eye condition which causes life-long vision loss to 2.3% of people aged 70 to 80, and over 12% of people over 80 years old.
What is AMD?
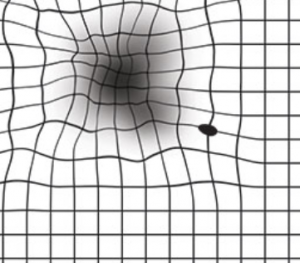
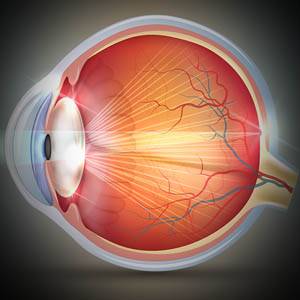
Age-related macular degeneration is a progressive disease of the retina — the light-sensing tissue at the back of the eye.
In later stages, advanced AMD can lead to permanent central vision loss and even blindness.
There are two main forms of AMD, known as Dry AMD and Wet AMD, each has its own cause and treatment. Advanced Dry AMD can lead to Wet AMD.
What is AREDS?
Two ground-breaking studies sponsored by the National Eye Institute have been done to evaluate the effect of nutritional supplements on the development and progression of age-related macular degeneration (AMD), these are known as the Age-Related Eye Disease Studies, AREDS and AREDS2.
The AREDS trials found that a formulation of specific vitamins and minerals can slow the progression of Dry AMD.
Furthermore, for those who have advanced AMD in one eye only, it can slow the progression of AMD in the other eye.
What is the AREDS Formula?
Based on the AREDS2 trial, the recommended supplement formulation was changed to:
- 500 mg of vitamin C
- 400 IU of vitamin E
- 80 mg zinc as zinc oxide
- 2 mg copper as cupric oxide
- 10 mg lutein
- 2 mg zeaxanthin
It is also recommended to add omega-3 fatty acids, especially DHA and EPA. DHA is necessary for the health of retinal cells and helps promote retinal development and repair.
According to the research, people at high risk for developing advanced AMD—those with intermediate AMD and those with advanced AMD in one eye only—had their risk of getting advanced AMD decreased by roughly 25% when treated with a combination of antioxidants and zinc and copper.
Here are some frequently asked questions about AREDS.
1. Are AREDS vitamins right for me?
According to the study, people with intermediate or late AMD benefited from the AREDS and AREDS2 formulas. However, people with early AMD or those who did not have AMD received no advantage.
Your eye doctor will be able to provide you with the best advice on how to manage your AMD.
SEE RELATED: Protecting Yourself From Macular Degeneration
Contact an eye doctor near you to discuss if AREDS supplements are right for you.
2. Can taking the AREDS supplements prevent AMD?
No.
The AREDS and AREDS2 supplements don’t prevent AMD.
However, the supplements may help you preserve your eyesight longer by delaying the advancement of intermediate to advanced AMD.
3. Can I take a daily multivitamin and the AREDS formula?
Yes.
Multivitamins are not a substitute for the AREDS formulas.
Two-thirds of AREDS participants also took multivitamins in addition to the AREDS formulation. In AREDS2, nearly 9 out of 10 people took multivitamins.
4. Does a daily multivitamin alone provide the same vision benefits as the AREDS formula?
No.
The vitamins and minerals used in the AREDS and AREDS2 studies were given in substantially larger amounts than contained in multivitamins.
Over and above multivitamins, taking an AREDS formulation clearly provided a benefit.
5. Can I alter my diet to have the same amount of antioxidants and zinc as the AREDS formula?
No.
High levels of vitamins and minerals are difficult to obtain via food alone. Previous research has found that people who eat a diet high in green, leafy vegetables, which are high in lutein and zeaxanthin, had a lower risk of developing AMD.
Those who benefited the most from taking lutein and zeaxanthin in the AREDS2 trial were those who did not get enough of these nutrients in their diet. When compared to those who did not take the supplements, study participants who took lutein/zeaxanthin supplements had a 26% lower risk of getting advanced AMD.
6. Can taking AREDS interfere with other medications?
High-dose nutritional supplements can occasionally interfere with medications and compete for absorption in the body with other essential nutrients.
People who are thinking about taking an AREDS formulation should prepare a list of all their medications to give to their doctor. All supplements and over-the-counter medications should be included on the list.
7. What are lutein, zeaxanthin, and beta-carotene?
Carotenoids are a group of nutrients that includes lutein, zeaxanthin, and beta-carotene.
Plants produce carotenoids, which are abundant in green leafy foods. They can be preserved in animal tissues and are found in animal-based meals at relatively low amounts.
The body converts beta-carotene into vitamin A, which is needed by the retina to detect light and convert it to electrical signals to the brain.
Lutein and zeaxanthin, on the other hand, are essential in the retina and lens, where they may act as natural antioxidants and aid in the absorption of harmful blue and UV radiation.
8. What are omega-3s?
Omega-3 fatty acids are found by marine algae and in certain fish oils.
These oils thought to be responsible for the health benefits of eating fish on a regular basis, such as a lower risk of cardiovascular disease.
LEARN MORE: Guide to Eye Conditions
Schedule an appointment with an eye doctor near you to discuss treatment for your AMD.
Macular degeneration (AMD) is an eye condition which causes significant vision loss to over 1 in 8 people over 80 years old.
The AREDS trials found that formulation of specific vitamins and minerals can slow the progression of AMD, this is known as the ‘AREDS formula’.